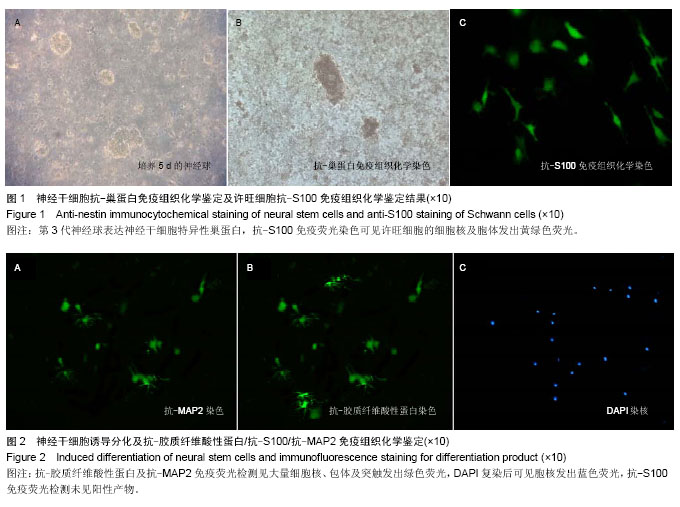
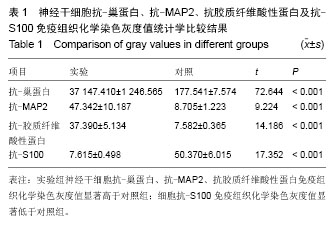
| [1] Noctor SC, Martínez-Cerdeño V, Ivic L,et al.Cortical neurons arise in symmetric and asymmetric division zones and migrate through specific phases.Nat Neurosci.2004.7(2): 136-144.
[2] 刘伟国,虞军,龚江标.大鼠胚胎神经干细胞的培养及分化的观察[J].江医学,2005,27(1):30-32.
[3] 曹李,张宇新.神经干细胞移植治疗的研究进展[J].人民军医,2012,55(3):266-267.
[4] Cui L, Jiang J.Transplantation of embryonic stem cells improves nerve repair and functional recovery after severe sciatic nerve axotomy in rats.Stem Cells. 2008; 26(5): 1356-1365.
[5] Xu L, Zhou S, Feng GY,et al. Neural Stem Cells Enhance Nerve Regeneration after Sciatic Nerve Injury in Rats. Mol Neurobiol.2012;46(2):265-274.
[6] Roy NS, Cleren C, Singh SK, et al.Functional engraftment of human ES cell-derived dopaminergic neurons enriched by coculture with telomerase-immortalized midbrain astrocytes. Nat Med.2006;12(11): 1259-1268.
[7] Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000; 287(5457): 1433-1438.
[8] Chojnacki A, Weiss S.Production of neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes from mammalian CNS stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(6):935-940.
[9] Tansey KE, Seifert JL, Botterman B, et al.Peripheral Nerve Repair Through Multi-Luminal Biosynthetic Implants.Ann Biomed Eng.2011;39(6):1815-1828.
[10] Liard O, Segura S, Sagui E,et al. Adult-brain-derived neural stem cells grafting into a vein bridge increases postlesional recovery and regeneration in a peripheral nerve of adult pig.Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:128732.
[11] 李峰,穆广态.外周神经损伤的显微外科修复[J].中华显微外科杂志,2004, 27(1):27-29.
[12] 蔡明,陆耀飞,娄淑杰.大鼠大脑皮层神经干细胞培养方法比较[J].神经解剖学杂志,2013,29(1):70-74.
[13] Riet ze RL, Valcanis H, Brooker GF, et al. Purification of a pluripotent neural stem cell from the adult mouse brain. Nature. 2001;412(6848) : 736-739.
[14] 王璐,何芙蓉.巢蛋白nestin在人甲状腺常见肿瘤组织的表达[J].实用肿瘤杂志,2010. 25(5):515-517.
[15] 张俊虎,王建交.神经干细胞的鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(27):108-5112.
[16] 张在金, 董艳, 卢亦成.大鼠胎脑不同部位神经干细胞比较性培养的研究[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2008, 7(4):325-327.
[17] 刘靖,曲静,徐晓静,等.神经干细胞迁移的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报.2012,34(3):201-211.
[18] 罗江兵,赵鹏洲,欧英雄,等.神经干细胞在脑损伤模型中的迁移、成活和神经生长因子表达[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2012, 17(5):232-234.
[19] 刘岚,张成.大鼠脂肪干细胞源性神经球分化为雪旺细胞样细胞[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2011,31(7):991-995.
[20] 万虹,安沂华.雪旺氏细胞促进共培养大鼠胚胎神经干细胞的分化[J].中华神经外科杂志,2002,18(2):100-103. |